Spring Security - Authorization
spring security主要解决三个问题:
- Authentication:认证。谁在访问;
- Authorization:权限。某用户能不能访问;
- protection:防止一些常见的攻击;
其实虽然spring security的authentication验证方法多种多样,但目的都是一样的——为了获取authentication。更确切地说,authentication里的user和password也只是验证前的基本信息,真正想通过验证获取到的是authorization。有了authorization,就可以对设置了权限的接口进行鉴权了。所以忙活了半天,鉴权才是正事儿。
Authentication中的核心概念
Authentication的主要概念大概有三部分:
- 怎么表示权限;
- 怎么设置权限;
- 谁来鉴权;
何谓权限
权限包含在Authentication里(所以由AuthenticationManager在设置Authentication的时候设置):
1
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
而GrantedAuthority就是简单地用string代表权限:
1
String getAuthority();
所以说白了,权限就是string。
在Spring Security - Authentication中介绍了一个很重要的概念:role和普通authorization没有明显区别,role是额外从authorization里分离出来的一个概念,谈及role的时候,它默认是ROLE_开头的权限。比如设置一个role pikachu,实际相当于添加了一个ROLE_pikachu authorization。
权限配置
配置权限的方式多种多样,给方法配置权限最常使用的是spel:@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('admin', 'pikachu')
方法权限是从方法上的@PreAuthorize注解里取的。实际权限从哪里取?自然是从http里取。Spring Security - 架构已经介绍了权限实际放在SecurityContextHolder里,它用ThreadLocal存储,所以全局可获取:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
static final Supplier<Authentication> AUTHENTICATION_SUPPLIER = () -> {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication == null) {
throw new AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException(
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext");
}
return authentication;
};
最后,spring security注解相关的权限配置需要手动开启,使用@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity或更新的@EnableMethodSecurity。
谁来鉴权 - AuthorizationManager
AccessDecisionManager会获取Authentication里的权限,用于鉴权。spring更推荐使用AuthorizationManager(主要应该是它支持泛型,待判断的对象不必用object表示)。感觉语义上和AccessDecisionManager差不太多,都是返回是否鉴权通过。
接口很简单,返回一个鉴权结果AuthorizationDecision:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
/**
* Determines if access is granted for a specific authentication and object.
* @param authentication the {@link Supplier} of the {@link Authentication} to check
* @param object the {@link T} object to check
* @return an {@link AuthorizationDecision} or null if no decision could be made
*/
@Nullable
AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, T object);
AuthorizationManager有很多实现,RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager是其中一个,用来判断一个http请求是否符合待校验的权限。它也只是一个代理实现,实际会委托给一堆AuthorizationManager,每个AuthorizationManager绑定一个RequestMatcher,如果当前http请求符合matcher,就使用这个AuthorizationManager鉴权。
常用的配置权限的方式是@PreAuthorize,所以spring security使用spring aop创建了两个method增强:
AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptorAuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor
提供对@PreAuthorize注解的支持。
其实就是调用方法之前先使用AuthorizationManager校验一下@PreAuthorize注解的那个方法的权限和http里的权限是否符合。这里用到的鉴权manager是PreAuthorizeAuthorizationManager,它提供了对“方法相关的鉴权”的支持(public final class PreAuthorizeAuthorizationManager implements AuthorizationManager<MethodInvocation>)
层级权限 role hierarchy
权限一般存在层级概念,比如admin一般都有普通user的权限。为了让user权限的方法也支持admin权限,实现的时候,
- 要么所有可以用user权限的方法都标上admin权限(太累了);
- 要么直接给admin赋予user权限,这样所有可以用user权限的方法,admin自动就能访问了;
RoleHierarchy就是为后者准备的。它就一个方法:
1
2
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getReachableGrantedAuthorities(
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities);
传入一个role(就是string),返回一个role数组,代表该角色拥有的所有角色权限。比如:
- 传入admin权限,返回admin、user,代表admin同时拥有user权限;
- 传入user权限,只返回user,代表user权限不包含更低级的权限;
RoleHierarchy的一个实现是RoleHierarchyImpl。允许传入这种格式的role层级:ROLE_A > ROLE_B > ROLE_C(实现的时候用大于号split字符串,解析为token),a包含b和c,b包含c。也可以使用\n拼接字符串,指定多条角色包含关系。
RoleHierarchyImpl对传入的string的处理方式就是:先按照\n把string分成好几条链,再逐一解析合并每一条链。
AuthorizationManager实际使用RoleVoter鉴权。RoleHierarchyVoter是RoleVoter的子类,获取权限的时候,使用RoleHierarchy获取(一串儿)权限。
RoleVoter的权限获取,只能获取权限本身:
1
2
3
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> extractAuthorities(Authentication authentication) {
return authentication.getAuthorities();
}
RoleHierarchyVoter的权限获取,可以取得本权限加上所有低层级的权限:
1
2
3
4
@Override
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> extractAuthorities(Authentication authentication) {
return this.roleHierarchy.getReachableGrantedAuthorities(authentication.getAuthorities());
}
所以我们配置一个自定义的RoleHierarchyVoter就行了。可以写成一条链,也可以像下面一样写成四条链:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@Bean
AccessDecisionVoter hierarchyVoter() {
RoleHierarchy hierarchy = new RoleHierarchyImpl();
hierarchy.setHierarchy("ROLE_ADMIN > ROLE_STAFF\n" +
"ROLE_STAFF > ROLE_USER\n" +
"ROLE_USER > ROLE_GUEST");
return new RoleHierarchyVoter(hierarchy);
}
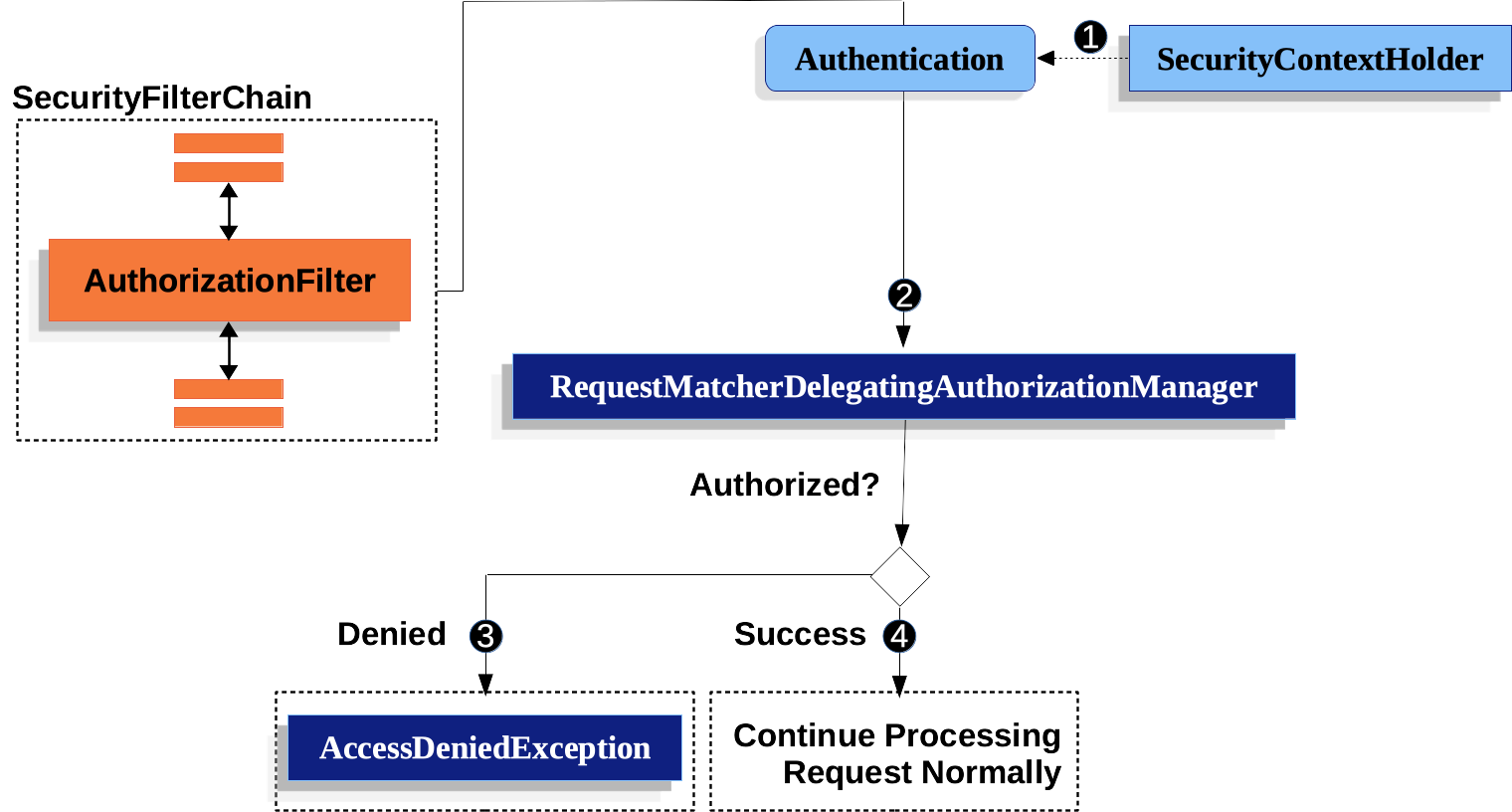
AuthorizationFilter
security filter chain上有一个filter是AuthorizationFilter,它提供了对url权限的校验。可以通过HttpSecurity#authorizeHttpRequests自定义配置修改默认行为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws AuthenticationException {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().authenticated();
)
// ...
return http.build();
}
它决定filter chain要不要执行下去的方式非常简单:就看AuthorizationManager返回的AuthorizationDecision是否通过,通过则继续:
用到的AuthorizationManager是RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager。
这个manager我们也可以自己配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http, AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> access)
throws AuthenticationException {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().access(access)
)
// ...
return http.build();
}
@Bean
AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> requestMatcherAuthorizationManager(HandlerMappingIntrospector introspector) {
MvcRequestMatcher.Builder mvcMatcherBuilder = new MvcRequestMatcher.Builder(introspector);
RequestMatcher permitAll =
new AndRequestMatcher(
mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/resources/**"),
mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/signup"),
mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/about"));
RequestMatcher admin = mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/admin/**");
RequestMatcher db = mvcMatcherBuilder.pattern("/db/**");
RequestMatcher any = AnyRequestMatcher.INSTANCE;
AuthorizationManager<HttpServletRequest> manager = RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager.builder()
.add(permitAll, (context) -> new AuthorizationDecision(true))
.add(admin, AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole("ADMIN"))
.add(db, AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole("DBA"))
.add(any, new AuthenticatedAuthorizationManager())
.build();
return (context) -> manager.check(context.getRequest());
}
感想
鉴权并不考虑SecurityContextHolder里的authentication哪来的,只管拿来用。怎么放进去是认证应该考虑的事情。spring security的分工做的还是挺明确的。