Elasticsearch:_source store doc_values
一切始于一个奇怪的现象:elasticsearch以epoch_millis存储时间戳的时候,竟然可以接受string(字面值为long)存储,且使用起来和long毫无区别:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
GET <index>/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"timestamp": {
"lte": "2",
"format": "epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}
GET <index>/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"timestamp": {
"lte": 2,
"format": "epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}
但是只能用long字面值的string,用其他string是不合法的。
而spring-data-elasticsearch在转换时间的时候,全都用的string,没有long。对于Instant的long,也是转换成了string格式。所以我在它那里提了一个issue。通过这个issue,也明白了另外一个之前困扰我的问题:为什么elasticsearch能够做到总是返回_source。
从date的文档介绍也可以看出来,elasticsearch在内部实际是使用string存储
epoch_millis的,即使传入的是long: Dates will always be rendered as strings, even if they were initially supplied as a long in the JSON document.
存储方式
elasticsearch的_search API有三种查询参数,对应了不同的查询方式:
其实对应了三种存储方式:
倒排和正排
一个索引包含多种存储结构,主要可以归结为倒排和正排两类:倒排用于检索,field to doc;正排用于获取内容,doc to fields。
倒排可以简单理解为一个hashmap,hashmap的value理论上是doc,实际上可以仅仅只有doc id。 正排有着不同的实现方式,可以是简单的行式存储,也可以是列式存储。
所谓行式列式:在存储在磁盘/内存的时候其实都是行式,但是如果这一行存储的是所有的文档的这一列(把列按行存),在逻辑上相当于一次能读写一列。所以把列按行存(行实际上存的是列的数据),就是列式存储。
假设有以下三个文档:
1
2
3
Doc1: { "name": "Alice", "age": 25, "city": "NY" }
Doc2: { "name": "Bob", "age": 30, "city": "LA" }
Doc3: { "name": "Charlie", "age": 35, "city": "SF" }
可以把他们看做行式存储,每一行一个doc。
列式存储会分别为每个字段存储其值和 doc_id 的关联:
name:{ 1: "Alice", 2: "Bob", 3: "Charlie" }age:{ 1: 25, 2: 30, 3: 35 }city:{ 1: "NY", 2: "LA", 3: "SF" }
第一行存的是每一个doc的name字段,第二/三行存的是每一个doc的age/city。
如果用数组下标表示doc id,那么可以更简化一些:
name:{ "Alice", "Bob", "Charlie" }age:{ 25, 30, 35 }city:{ "NY", "LA", "SF" }
不过这种方式不太适合稀疏数据。
所以列式存储的时候,不同文档的相同field(逻辑上的一个列)的值存储为一行(对应为上述一个数组),列式存储更适合按照列值做排序和聚合。当只需要返回这个列的值时,可以从这里直接读取所有列的值(实际上是在读行)。
The value of the same fields for different documents are stored all together consecutively in memory and it is possible to access a certain field for a certain document “almost” directly.
如果使用列式存储,如何通过正排索引方便地获取doc所有的field? 毕竟列式存储更适合获取所有doc的某个field,不适合获取一个doc的所有fields。所以elasticsearch做了一些其他的工作:内部保留一个_source字段,需要取完整doc时,直接从这里取。
_source field
elasticsearch默认会把原始文档存成一个名为_source的field,作为elasticsearch创建的文档结构的一部分,如果查询的时候没有什么特殊参数,返回的是符合条件的文档的_source字段(而不是这个文档的全部)。
_source是store类型的字段,对用户透明。
store
store是field的一个属性,默认store=false,即:field不单独存储到文档里。假设field的index属性为true(默认),这个field会出现在倒排索引里,所以field可查询。但是查询到这个文档后,返回的是_source field,是整个文档,而不是单独的某个字段。
如果不想返回整个_source,只想返回某个字段,可以在查询的时候使用_source option从_source里获取。
返回的是
_source里该字段的原始值。
虽然直接返回_source是很快的,但是想从_source里取某几个字段,速度自然就变慢了。如果_source太大(比如有个context字段存了一篇文章),而经常用到的请求都只是查其中的小字段(比如title),那么可以给title设置store=true,只查title,且直接返回title。
这是典型的以(存储)空间换(查询)时间,一般情况下不太用得到。
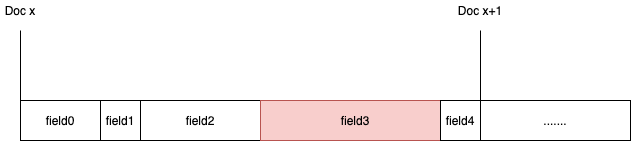
Lucene的store
stored是Lucene里的概念:一个index=true但是stored=false的字段能被搜索到,但不在最终的返回结果里。如果所有字段都只index不stored,最终返回的只有一个文档id。用户可能会拿着这个id去其他数据库比如mysql获取完整数据。
- https://stackoverflow.com/a/32952682/7676237
elasticsearch的store使用的就是Lucene stored的概念,_source是elasticsearch文档的第0个store=true的field。store的field是row manner:每一个field在elasticsearch的document里顺次排列。
elasticsearch返回store字段比返回_source里的某个字段速度快的原因也一目了然:field的寻找时间变快了,只需要返回每个命中的doc从起始位置偏移x个字节后的field就行了,无需加载_source并解析里面的field。
以空间换时间。
doc_values
doc_values原本是为了排序和聚合用的,但因为它使用了额外的空间存储field(这一点比较像store),所以在搜索的时候如果只需要返回这一部分的field,可以直接从doc_values存储的地方读取。
多占用的空间不能浪费,也可以拿来换时间!
index是构建一个倒排索引,是key to value的map,value就是doc。搜索是知道key,找value,也就是找doc。但是排序和聚合是知道doc找key,也就是按照value找key,所以按理说得搞个value to key的map。
doc_values的文档开头详细介绍了这一点:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.4/doc-values.html先不考虑一个key有多个value的问题。
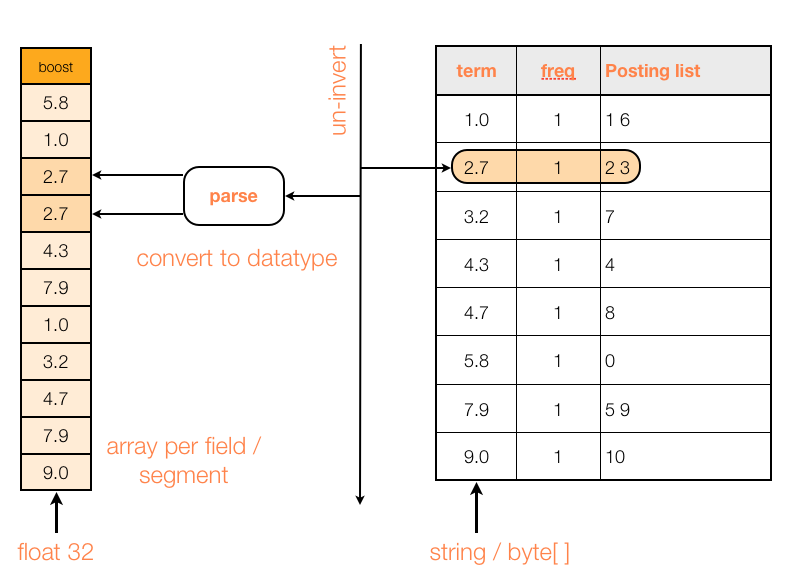
Lucene的doc_values
Lucene的doc_values是把倒排索引(key to value)倒过来(value to key),英文叫 univert the inverted index,“把倒排索引倒过来”,中文称之为正排索引。
Lucene用一个数组实现了这个value to key的map,数组的下标本身代表了doc的id(Lucene id,不是elasticsearch id):
doc_values的结构是列式存储。 正排索引一开始使用的是fielddata,放在内存里,后来才发展成了doc_values,放磁盘里:
- elasticsearch从
fielddata到doc_values的发展:https://www.elastic.co/cn/blog/elasticsearch-as-a-column-store - Lucene的
doc_values:https://blog.trifork.com/2011/10/27/introducing-lucene-index-doc-values/
关闭index
关闭index并非就不能查找了,如果开启doc_values也是可以的(doc-value-only field),可查,但查的比index要慢,而且可聚合,尤其适用于那些不怎么用于查找、过滤的统计field。
Query performance on doc values is much slower than on index structures, but offers an interesting tradeoff between disk usage and query performance for fields that are only rarely queried and where query performance is not as important. This makes doc-value-only fields a good fit for fields that are not expected to be normally used for filtering, for example gauges or counters on metric data.
如果只想把数据存到_source里,直接index=false + doc_value=false,应该更省空间:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.4/mapping-index.html
range查询
数值范围查询用的是正排,不过字段使用了Lucene 的 PointValues 实现。它的底层原理是BKD树(Block KD-Tree),可以很粗糙的理解为多维的B+树,如果数据是一维的(比如age),就简单理解为B+树,可以做范围查询。BKD树的优势是可以拓展到多维,以支持地理位置等数据。
排序和聚合查询
排序和聚合也用到了正排,因为doc values的正排是列式存储,所以很适合直接取所有列的值,然后应用排序或聚合算法。
查询
查询之所以有不同的方法,其实就是因为field存储的位置不同,我们实际上是在使用不同的查询参数告诉elasticsearch去不同的地方查询:
- https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.4/search-fields.html
从不同的地方查:
fields或默认的_source: 从_source查;store: 从store=true的field查;doc_values: 从doc_values=true的field查;
_source过滤查询
_source过滤查询,从_source查特定的字段,所以要解析_source。返回的field和_source里存入的值相同。
fields查询
同样是从_source获取特定field,但是返回的值并不是原始值,而是使用mapping解析后的值:
- 从
_source取field的值; - 使用mapping解析值;
The fields option returns values in the way that matches how Elasticsearch indexes them. For standard fields, this means that the fields option looks in
_sourceto find the values, then parses and formats them using the mappings. Selected fields that can’t be found in_sourceare skipped.
正因如此,在开篇的例子中,date的内部使用string存储,所以即使epoch_millis存储的时候值为long,在通过fields查询时,也会返回string而非long:
- https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-data-elasticsearch/issues/2318#issuecomment-1264448733
假设updateTime和timestamp两个field都是epoch_millis类型,存入的都是long而非string:
1
2
3
4
5
GET <index>/_search
{
"fields": ["updateTime", "timestamp", "likes"],
"_source": ["updateTime", "timestamp", "likes"]
}
结果fields返回的是string,_source返回的是存入时的long:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
{
"_index" : "<index>",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1310454-zs_KVugpMxs",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_routing" : "1310454",
"_source" : {
"updateTime" : 1663094372553,
"timestamp" : 1662999708000,
"likes" : 18
},
"fields" : {
"updateTime" : [
"1663094372553"
],
"timestamp" : [
"1662999708000"
],
"likes" : [
18
]
}
},
官方认为fields查询比_source查询有一些优势。由于它用到了mapping,所以能:
- 规范化返回数据:比如上述
epoch_millis既存储了long又存储了string,就可以使用mapping统一返回string; - Accepts multi-fields and field aliases
- Formats dates and spatial data types
- Retrieves runtime field values
- Returns fields calculated by a script at index time
- Returns fields from related indices using lookup runtime fields
暂时只用到了第一条优势。2023-05-19:现在也用到runtime field了。
因为会用到mapping,所以对于runtime field这种实际没有被index的数据,虽然_source里没有该field,但是使用fields查询可以把它查出来。
自定义转换:runtime field
fields只能按照mapping进行转换,正常情况下没什么问题。但是如果有特殊的需求,比如fields只能让epoch_millis以string返回,如果我们就想让它以long返回,可以使用runtime field转换数据,再用fields查出来:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
GET <index>/_search
{
"runtime_mappings": {
"wtf": {
"type": "long",
"script": {
"source":
"""emit(Long.parseLong(params._source['timestamp'].toString()))"""
}
}
},
"_source": false,
"fields": [
"wtf"
]
}
返回的是long:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 15,
"successful" : 15,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "<index>",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "gHz4xIMBiDkSEf3Uym3G",
"_score" : 1.0,
"fields" : {
"wtf" : [
1633429574000
]
}
},
{
"_index" : "<index>",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "Znz4xIMBiDkSEf3UEG2_",
"_score" : 1.0,
"fields" : {
"wtf" : [
1622749174000
]
}
}
]
}
}
stored_fields查询
stored_fields查询,直接查stored字段。
官方文档说的很清楚,不建议用store,可以使用上述_source过滤查询取代store查询:
The
stored_fieldsparameter is for fields that are explicitly marked asstoredin the mapping, which is off by default and generally not recommended. Usesource filteringinstead to select subsets of the original source document to be returned.
如果field没有设置store=true,查询会被忽略:
If the requested fields are not stored (store mapping set to false), they will be ignored.
docvalue_fields查询
如果只查doc_values=true的列,docvalue_fields查询也会很快。
docvalue_fields存储的内容和_source一样,但查询比_source轻量,毕竟不需要加载整个_source。而且doc_value默认为true。反正就算不查它,空间也已经占用过了。
script_fields查询
script_fields查询建议使用runtime field取代script fields查询:Elasticsearch:runtime field
介绍了这么多,顺便把script_fields也介绍了。
上面说的基本都是空间换时间,script_fields是典型的时间换空间:不需要存,但每次查的时候都要临时计算。如果临时用一用,还是挺不错的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"script_fields": {
"test1": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "doc['price'].value * 2"
}
},
"test2": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "doc['price'].value * params.factor",
"params": {
"factor": 2.0
}
}
}
}
}
也可以用script获取_source里的field:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"script_fields": {
"test1": {
"script": "params['_source']['message']"
}
}
}
doc['my_field'].value:会把field缓存到内存里,所以更快,但需要占用内存;params['_source']['my_field']:每次都从_source里解析,所以慢,但省内存;
脚本
在从painless脚本里访问文档的字段时,也因为存储类型不同,产生了不同的访问方式。
只有doc_values字段才能用doc['xxx']访问,其他的只能去_source里取:params._source.xxx。如果是stored fields,可以使用params._fields['xxx']。
同样的,能用doc values就尽量不用source。source本身就是stored fields所以和其他stored fields速度差不多。除非source过大,这时候读取整个source再从里面提取field的速度要慢于直接的stored fields。
但是使用doc要做双重判断:
- 判断key存在:
doc.containsKey('xxx') - 判断值存在:
doc['xxx'].size() > 0
然后才能安全取值:doc['xxx'].value,非常麻烦。es8推出了field() API,来简化这个问题。但是目前还没有稳定。
params
在Elasticsearch的Script脚本中,可以通过params参数访问以下变量:
- params._source:表示文档的原始源(source)。
- params._fields:表示文档的字段(fields)。
- params._now:表示当前时间戳。
- params._score:表示文档的得分(score)。
- params._index:表示文档所在的索引(index)。
- params._type:表示文档的类型(type)。
- params._id:表示文档的ID。
- params._version:表示文档的版本号(version)。
- params._routing:表示文档的路由(routing)。
- params._parent:表示文档的父文档(parent)。
- params._now:表示当前时间戳。
- 除了以上预定义的变量外,还可以通过自定义的params参数传递其他变量给脚本使用。
没找到相关资料,以上回答来自chatgpt。
查询速度比对
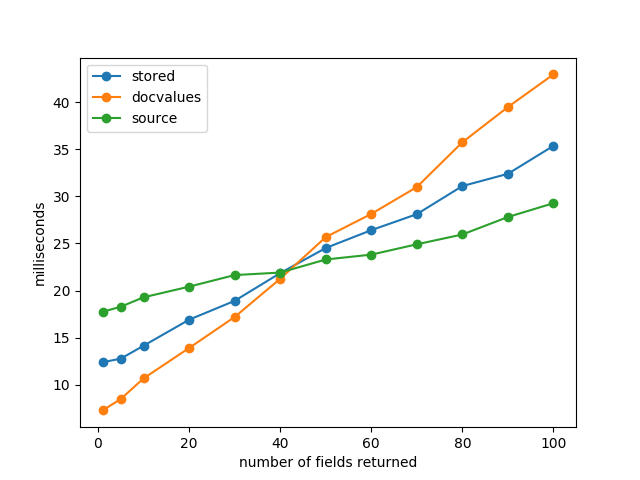
一个实验:
- https://sease.io/2021/02/field-retrieval-performance-in-elasticsearch.html
可以看出,需要取出的fields比较多的时候,使用_source更快,需要取出的fields较少时,从doc_values取更快。
store以行的方式存储,取的fields少的时候,不如doc_values直接把所有文档的整个field域的值(逻辑上列式存储的优势)取走快,但是如果取的fields比较多,相当于遍历所有fields了,doc_values的优势就没了。当然官方建议不用store,除非存储非常充足,否则没必要单独存一遍,直接用_source就行了。
所以:取的field较少时建议使用doc_values,取的多(实验中是40+个fields)建议使用_source。土豪可以考虑开store。
感想
- Lucene还是要看一看的;
- elasticsearch的实现也是要看一看的,正好又是Java实现的;
这篇文章是国庆在周口写的~